Genetic algorithm for optimization applied in game strategies.
Currently artificial intelligence has been applied in online games with the goal of generating a greater similarity with the real world. Artifical intelligences are usually applied in interactions with agents of the game or to create an enemy in order to defeat us.
Genetic Algorithms
Genetic algorithms belong to a class of techniques inspired by the evolution of species (species survival theory - Darwin) that aim to solve complex optimization problems. Usually the class of problems that the genetic algorithms aim to solve have an extremely high processing time to find the best solution using exact methods, which makes them unviable for scenarios that require quick answers. In this way, genetic algorithms try to provide optimal or very close to optimal solutions in a shorter execution time.
Clash Royale
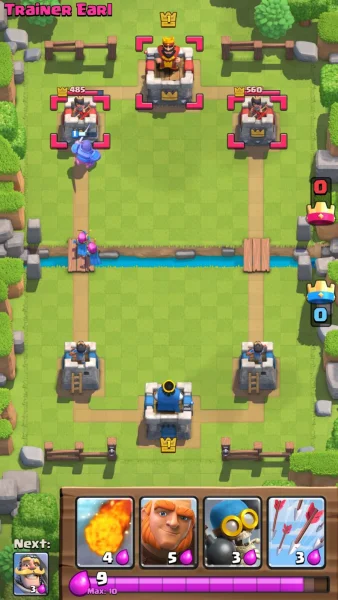
Clash Royale is a strategy game based on sequential positioning of cards in the arena with the goal of knocking down the towers of the enemy. The cards can only be positioned in the conquered spaces, and each card has a unique logic that describes its interaction with the arena. In the example figure below, the blue player played two cards that advanced across the bridge in the player’s red area in order to destroy the tower. In addition to the positioning, each card has a cost of elixir to be cast, so as the time goes and the elixir of the player is filling then the cards can be released.
Problem
How to define the best play to be made at each moment of time in the current state of the arena in order to maximize the difference between lost life and life taken?
Methodology
The method used to solve the problem of determining the best play every second of time is based on the current state of the arena calculated by a genetic algorithm. All Java source code is available in the following Github.
Simplified game modeling
In order to be able to perform the genetic algorithm tests, it was necessary to recreate the game in a much simpler scenario, so the following classes in java represent the structure of the game with the following assignments:
- Arena: It has a width and height that the cards can be throw, is also composed of a list of warriors representing the agents fighting to destroy the towers, and has a list of players that has same areas size of the arena to play the cards (usually two players, and each one has half the arena).
- Player: Has the limits of the arena that can use to cast its cards, has the amount of accumulated elixir that will be used to launch new cards, has the sequence of cards that will be thrown with the position in the arena (x and y axis), and also has a Tower that when destroyed means the defeat of the player.
-
Warrior: It represents the generic actions of a warrior. A warrior when thrown in the arena has the goal of going towards the enemy tower or the nearest enemy warrior and destroy it, if an enemy is not under his radius of attack he approaches the same to be able to annihilate it. There were modeled 6 types of warriors:
3.1. Dragon: It has a medium cost, attacks warriors and towers, is a flying card, has medium life, takes little damage, and has a medium range radius.
3.2. Giant: It has a high cost, attacks only the tower and not warriors, is a land card, has high life, takes a reasonable damage and has small range.
3.3. Minipeka: It has a medium cost, attacks warriors and land towers, is a land card, has medium life, takes a lot of damage and has a small range.
3.4. Musketeer: It has an medium cost, attacking towers and land and air warriors, is a terrestrial card, has low life, takes medium damage and has long range.
3.5. Skeleton: It has a low cost, attacking towers and land warriors, is a ground card, has very low life, low damage and small range.
3.6. Witch: It has an medium cost, attacking towers and land and air warriors, it is a terrestrial card, has medium life, low damage, average range and invokes skeletons every 5 elixir.
Initialization
With the cards and scenario modeled, now the main code responsible for bringing a match to life will be displayed. The match takes place within a cycle of iterations, at each iteration all the warriors in the arena advance one step, at that step each warrior executes his heuristic and searches the nearest enemy, then he checks the distance from the enemy found and decides based in the range if he will move a cell toward the enemy or perform a stroke of damage to take his life. At each iteration each player performs the following actions: the elixir of the player is increased by one, if the player has enough elixir he plays the next card of the sequence of cards, increases the counter to the next card of the sequence and decreases the cost of the last one card from your current elixir. When the last card of the sequence is played, the counter returns to the starting position and three options can be taken in relation to the new sequence of cards:
- The sequence is not changed and the same moves are made.
- Dynamically create a new list of cards and positions.
- The genetic algorithm is executed to define the new sequence of cards and positions.
Genetic Algorithm
The Genetic Algorithm in turn has the goal of calculating the next best sequence of cards at a given moment of time for a given arena state. The algorithm does this through a population of popsize size, where each individual represents a clone of the arena in the current state and the chromosome is given by the pairs of cards and positions of the sequence of cards of the player to be evolved. When a genetic algorithm is instantiated for the first time, it receives the reference of the arena where the real game is running, and through that it has access to the current state of the game. So for a given moment t and a given state s the genetic algorithm creates a population of size popsize by cloning the state s of the current arena at time t for all individuals. In this population the first player of the arena maintains the sequence of cards currently being used by the player in the current arena, and the others are restarted randomly. With this, the process of evolution of the algorithm that executes k generations is started, for each generation the fitness of each individual of the population is calculated and the best individual with greater fitness (maximization problem) is stored. After that, the variation operators are applied to generate the new descendants (popsize - 1). For each decendant two parents of the current population are selected by applying the tournament method (the tournament is done with the size of 20% of the value of popsize) and executed the crossover process between them with two cut points to set the exchange of genes and generate the offspring, with the new offspring generated, the mutation process is applied with a probability of 1.5% for each gene to replace the card and the position randomically. After the new population of offspring has been generated, the old population is replaced and the next generation initiates the process again, this process is repeated until it reaches the criterion of stopping k. In the end the best individual from the last population will be used to define the next sequence of cards and player positioning online. The fitness function of the algorithm performs for each cloned arena a separate execution considering a time advance of l iterations. After the iterations have been completed, the algorithm calculates the difference between the given damage and the damage received, the ultimate goal of the algorithm is to try to maximize this difference. To speed up the simulation process, as each arena is independent, popsize threads are created to do the sand calculations in parallel.
Conclusion
We can see in the video below an example of simulation of the algorithm in practice, the blue player is using the genetic algorithm while the red player is using a random logic (baseline).
References
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Genetic_algorithm
https://clashroyale.com/